Clinical and radiographic evaluation of MS implant placed in mandibular incisor area with immediate loading: A retrospective study.
By: Kwantae Noh, Jina Oh, Yong-Jin Kim
Introduction
In the past, the outcome of restorative treatment with implants in mandibular anterior region was dubious and poor in appearance. The mesiodistal crown diameter is as little as 5~5.5 mm and the cervical crown diameter is as little as 3.5~4 mm in the mandibular anterior region.
In addition, the space is often crowded and narrow by the continuously mesial moving due to its nature. Therefore, the two stage implant with 3.5 mm diameter, also called a mini-implant, which was formerly on the market, was not easy to stably install due to the shortage of bone mass and limitations in physical properties.
In addition, the esthetic outcome was poor.
However, the mandibular anterior region has some benefits including an arch shape allowing relatively stable occlusion and hard bone quality allowing immediate loading. Therefore, a more proper implant for this region is urgently needed based on these considerations.
Anatomical condition of mandibular anterior region
An implant with a diameter of 3 mm or less is required for installation in a mandibular anterior region with a missing tooth, and mechanical intensity should be properly maintained at the same time Since immediate loading or provisionalization may be needed in many cases for esthetic reasons, one body implant could be prefered in mandibular anterior region.
This one body narrow diameter makes it easy to conduct flapless surgery and requires bone grafting with relatively less frequency. In particular, hard bone quality is greatly beneficial for the initial implant stability and allows immediate loading in the mandibular anterior region.
In addition, implant installation equipment should be small enough not to bother the neighboring tooth because the mandibular anterior space is often crowded and narrow.
The purpose of this retrospective study was to evaluate clinical and radiographic outcome of mini-onebody implant placed in mandibular incisor site with immediate provisionalization.
Materials & Methods
Study participants
Thirty-four patients(20 men, 14 women; mean age 60.6) were selected from a group of patients treated with implant-supported prosthesis at one clinic. Informed written consent, approved by the Ethics Committee of the University of KyungHee, was obtained from patients to use their data for research purposes. The patients were followed for a median of 22months (range, 10 to 50months) after loading.
Implant
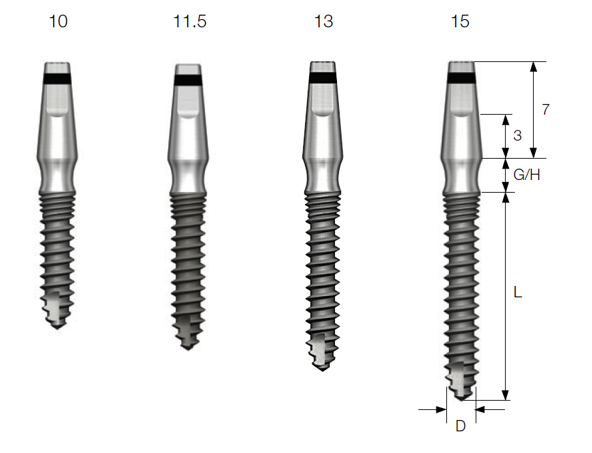
MS implant produced by Osstem (Korea) is suitable for areas affected by buccolingual width and mesiodistal width such as in the mandibular anterior region. Since the fixture and abutment is contained in one body, low cost is an additional benefit. Fixtures with diameters of 2.5 mm and 3 mm are available, and recommended installation torque is approximately 30Ncm.
Surgical and prosthetic procedure
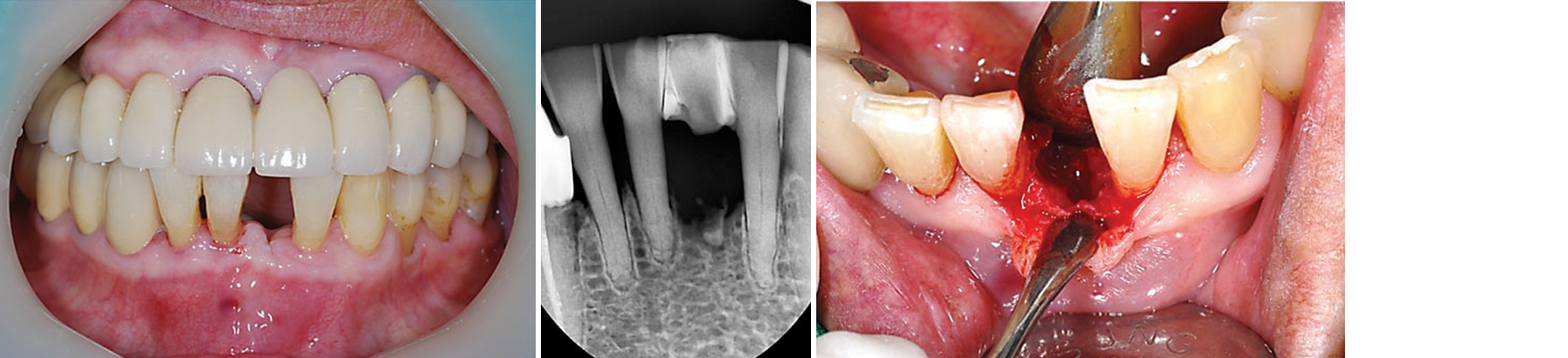
Fig. 1-3 Mucoperiosteal flap was elevated through a crevicular incision and root rest was extracted.
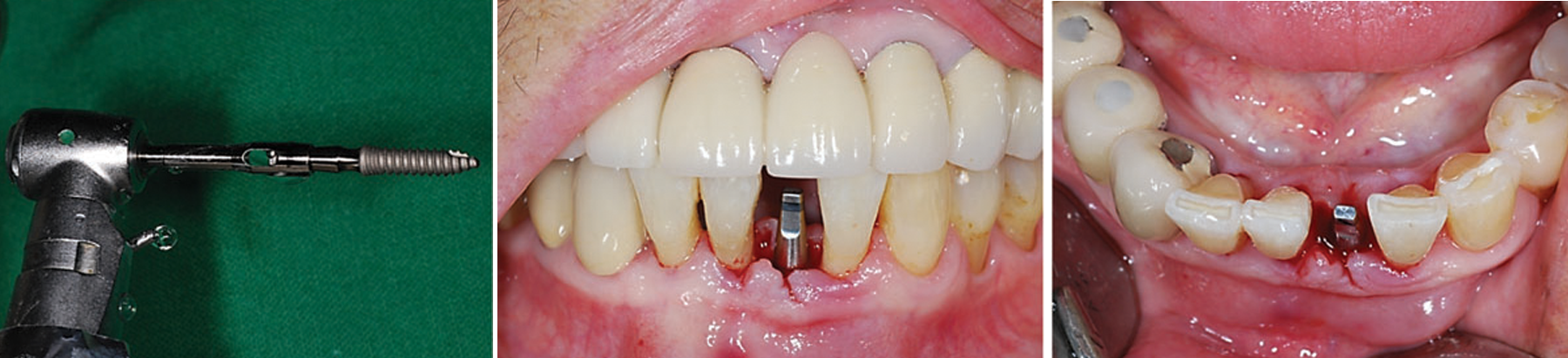
Fig. 4-6 Initial drilling was started with a sidecut drill. MS implant 3.0x11.5mm was placed and insertion torque was 25Ncm.
Fig. 7-9 Provisionalization was done immediate post-operatively with MS temporary cap.
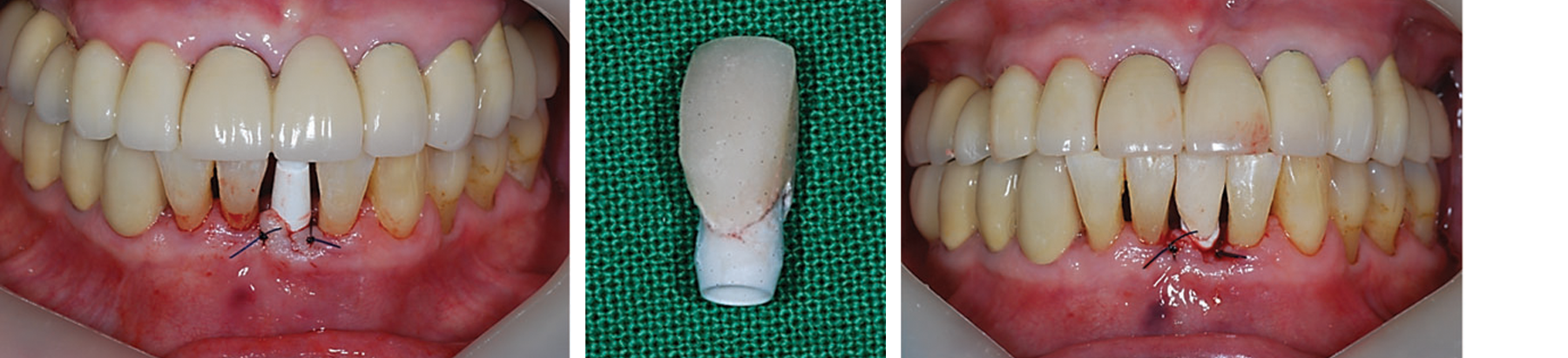
Fig. 10-12 Final prosthetic treatment was finished at POD 6 weeks. Soft tissue around the MS implant looks so healthy and harmonious with adjacent teeth.
Results
Implant survival
Two of the 54 MS implants were lost in 2 patients, giving a cumulative survival rate of 96.2%

Periapical radiograph 2years following insertion of definitive prosthesis
Conclusion
As reviewed above, since MS implant, a one-body implant system, is designed based on the considerations of physical properties needed for occlusion suitable for regions where buccolingual width and mesiodistal width is narrow, it is beneficial for the implant repair of single missing teeth in the mandibular anterior region in terms of both esthetic aspects and cost-effectiveness.
So, one body & narrow diameter implant, such as MS implant can be valid alternative in many clinical situations in which space problems do not permit the use of standard-diameter implants.
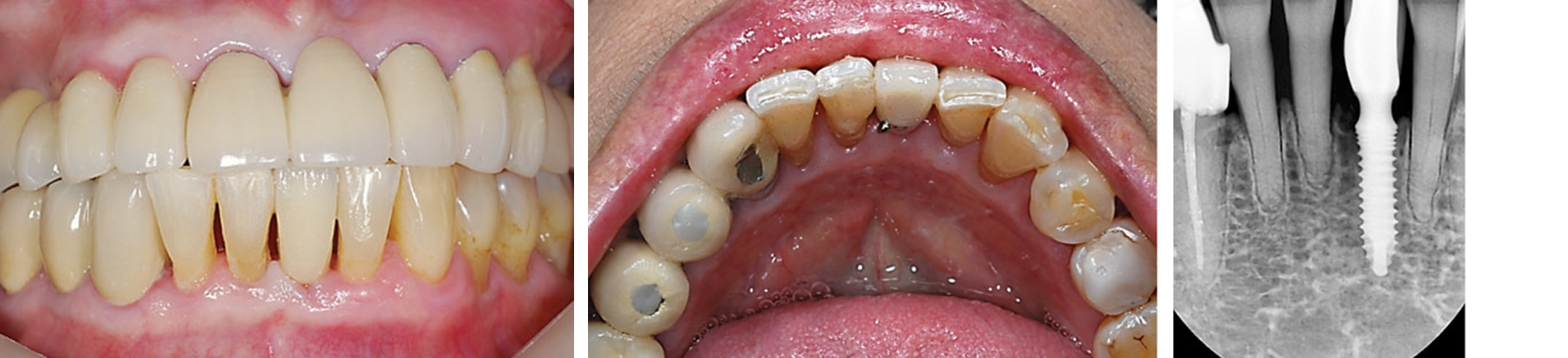
 Periapical radiograph 2years following insertion of definitive prosthesis
Periapical radiograph 2years following insertion of definitive prosthesis