Alveolar bone reconstruction using TSIII and Titanium mesh : a case report
By Ki-Ho Kim, Hyun-Woo Kim, Hwa-Sun Lee, Byung-Ok Kim, Sang-Joun Yu
Introduction
Reconstruction of the bone defect is an important factor in implant installation. Of the many techniques that are introduced, GBR (Guided bone regeneration) is most commonly used.
Wang et al. proposed a PASS principle for the predictable GBR, of which ‘space creation / maintenance’ is a difficult principle to fulfill in large bone defects.
GBR using titanium(Ti)-mesh has the advantage of ‘space creation / maintenance’ in the reconstruction of large bone defects due to the firmness of Ti-mesh.
In this case report, GBR using Ti-mesh technique and its follow-up of a patient with a large vertical and horizontal bone defect is presented.
Case Description
A 53 year-old male patient was referred for multiple implant in the lower jaw (#36,37,46,47) and upper jaw (#17,16,12,22,23,25,26,27).
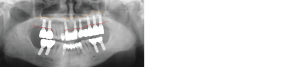
Fig.1. Panoramic radiograph at initial examination Alveolar bone loss is observed in multiple teeth and the post is exposed at #23 due to crown fracture.
Fig.2. Extraction of teeth and implant installation at the lower jaw The planned pre-implant area of the upper jaw shows severe vertical and horizontal bone loss.
Fig.3. 3D model using computerized tomography after placing upper stent A large vertical and horizontal bone reconstruction is needed for implant.
For the reconstruction of the large bone defect of the upper jaw, GBR with maxillary sinus lift was performed on each side. Allograft(Allo-Oss, CG Bio, South Korea) was used for bone graft.

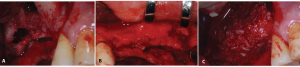
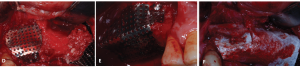
Fig. 4. Maxillary sinus lift and GBR #16,17 (A,C,E). #12,22,23,25,26,27 (B,D,F) A-B: Bone defect before surgery C: Repair of bone defect using Allograft-PRF mixture D-E: Fixation of Ti-mesh with bone tack after repair with graft material F: Fixation with bone tack after applying an absorbable membrane on the Ti-mesh G: Panoramic radiograph after maxillary sinus lift and GBR
Based on the CT analysis at 6 months post-operation, a vertical bone augmentation of 4.1-7mm and a horizontal bone augmentation of 5.7-12.4mm was shown. For the horizontal bone augmentation, a maximum of 2mm of graft resorption was observed.
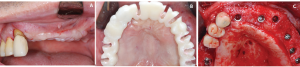
Fig. 5. 1st surgery after Ti-mesh removal after 6 months A: Vertically reconstructed alveolar ridge can be observed B: All the stent holes are placed within the reconstructed arch C: Implant(Osstem TSIII, Osstem Implant, South Korea) installation after Ti-mesh removal. All implants were installed at 1-1.5mm below the crest with more than 3mm of bone at the buccal side
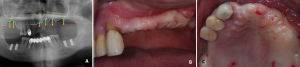
Fig. 6. Final prosthesis Final prosthesis was placed after using temporary teeth for 8 months while no change in the alveolar crest level was observed. The patient is currently being follow-up for 4 months after placing final prosthesis.